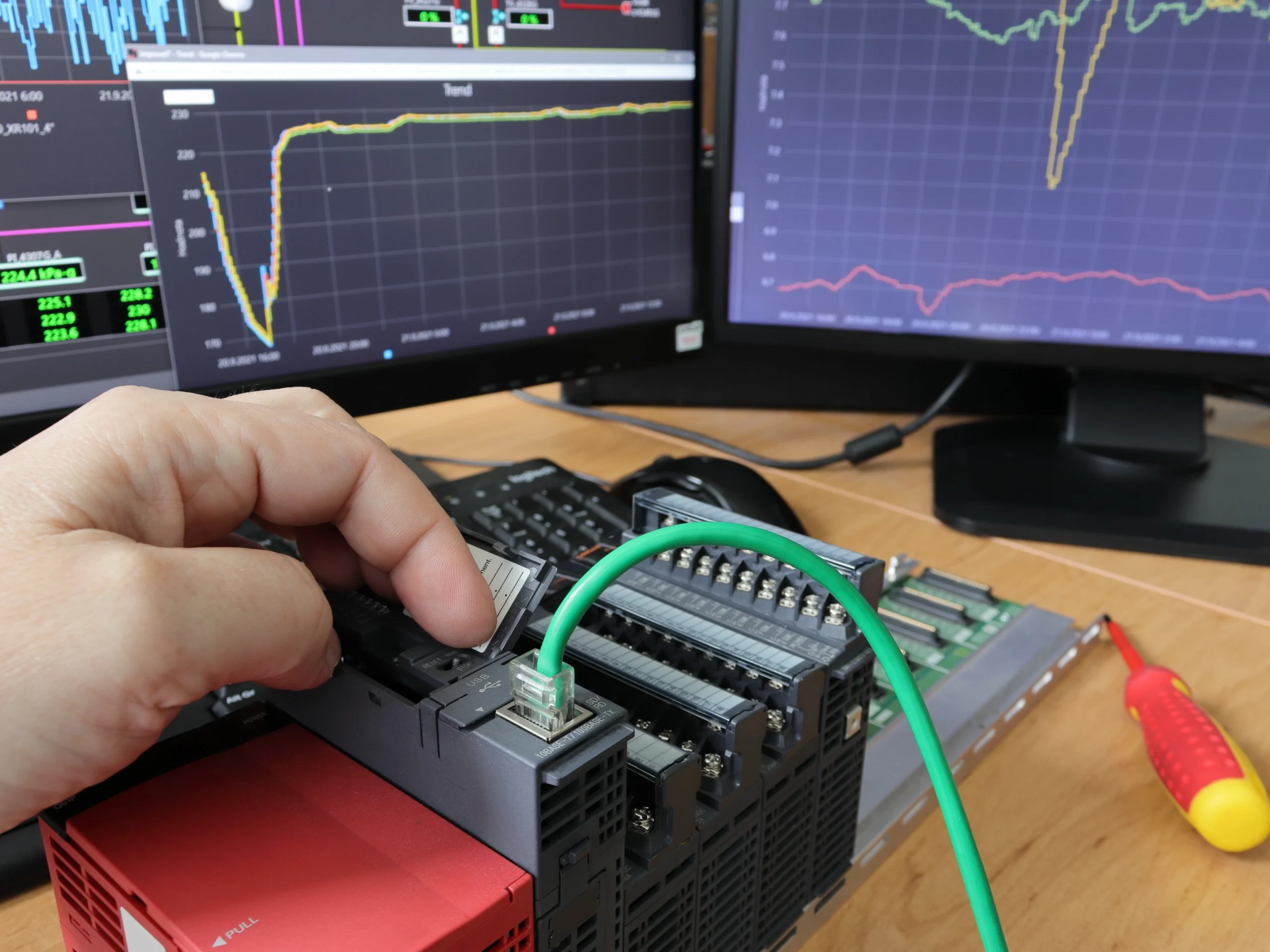
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) consists of a powerful Automation framework that enables organizations to collect, process, and analyze large amounts of data to transform industries by improving performance and efficiency. With advancements in technology, IIoT is becoming more accessible and relevant across industries.
Nearly every single organization across sectors globally have implemented IIoT, and 82% of those have gone beyond the testing phase and incorporated IIoT technology into their existing systems. Out of these adopters, two-thirds outsource a portion of their implementation—and only 38% trust that they can confidently execute it all internally. Outsourcing the Internet of Things (IoT) solution offers multiple advantages, such as greater efficiency and fewer risks. In comparison to choosing to build solutions internally, there are lesser chances for human errors, enhanced safety measures, and minimized business-related problems. A considerable fraction of firms find it too intricate to implement IoT independently due to the corporate transformation that is required for this purpose. Therefore outsourcing IoT solutions is a simpler execution strategy!
To ensure the successful execution of Industry 4.0 within your organizations, it is necessary for engineers and decision-makers to be well aware of the technical details of IIoT, the components involved, how they are connected, and the associated challenges and security risks. In this article, we will discuss in-depth the key components and the four layers of Industry 4.0 technology that are paramount for a smooth transition into a ‘Smart Industry’.
Note that the four-layered IIoT architecture is a high-level framework and remains consistent regardless of industry. Whether you are involved in manufacturing automation, mobility automation, construction automation, energy, or oil and gas automation — this framework will still apply.
Industry 4.0, IIoT, and Smart Factories:
The concept of Industry 4.0 or Industrial Automation is also known as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), smart manufacturing, and connected factory – just to name a few!
Over the past decade, we have welcomed this new model of industrialization (Industry 4.0), where companies are utilizing cutting-edge IoT solutions such as cloud technology, data analytics, and AI to revolutionize their processes and products for the better. Smart Factories employ this latest wave of tech advances to innovate production methods while—the Smart Product—incorporates internet-based and value-added services to offer its customers.
One example of a ‘Smart Product’ is Amazon’s Alexa, which utilizes the internet and Artificial Intelligence to create an electronic voice-assistance service. A ‘Smart Factory’, on the other hand, applies automated process lines and sensor-based monitoring, AI-powered decision-making based on data analytics models, plus other cutting-edge technologies – all in order to replace manual work. It is up to each industry as to how many smart strategies they implement; thereby entitling their company with this highly sought-after title of being known as a true “Smart Factory”.

The Four-Layered IIoT Framework:
To understand the complex structure of industrial IoT, it is essential to recognize four components: devices/equipment, networks, cloud services, and applications. These all divide into the Perception layer (devices/equipment), Network layer (connectivity), Processing Layer (cloud services), and Application Layer (applications). These four layers compose the comprehensive framework of an IIoT model, which works together to streamline industrial automation processes.
A well-designed Industrial Automation solution, based on the IoT framework has the potential to transform various industries by providing real-time insights into industrial processes, optimizing performance, and improving efficiency.
#1 Perception layer:
This layer is a combination of physical components such as sensors, security cameras, actuators, I/O devices, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), robots, and alarm systems that work together and are responsible for collecting data from sensors and other industrial devices. Typically, they collect data about various physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vibration from industrial devices such as machines, robots, and sensors. These components are built robustly and form the first layer or foundation for on-field automation activities such as tracking, monitoring processes, or mobilizing activities.
The key functions of the Perception layer in an IIoT Solution include:
- Data acquisition: Collecting data from sensors and other industrial devices.
- Data filtering: Filtering and cleaning the raw data to remove noise and inconsistencies.
- Data conversion: Converting the raw data into a digital format that can be transmitted over the network.
- Data preprocessing: Preprocessing the data to reduce its size and optimize its format for transmission.
- Device management: Monitoring and managing the performance and availability of the devices in the perception layer.
A well-designed perception layer can help organizations to gather and analyze data quickly, enabling them to react faster to changes in the environment and make better-informed decisions.
#2 Network layer:
This refers to the layer of communication protocols and incorporates a variety of connectivity networks such as WiFi/IEEE 802.15.4, Bluetooth, LoRa, 6LoWPAN, and NarrowBand-IoT to enable data transfer between industrial devices to the next layer of Processing systems. Industrial Ethernet sets up this layer’s foundation as it sends information to a cloud and components in the Processing layer for further utilization.
The key functions of the Network layer an IIoT Solution include:
- Device connectivity: Connect devices, sensors, and other endpoints to the IIoT network.
- Data routing: Determining the optimal path for data to travel between devices and applications.
- Data transmission: Transmitting data between devices and applications using various protocols such as RS485, Modbus, MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP.
- Security: Ensuring that data transmitted over the network is secure and encrypted.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Managing the network traffic and ensuring that data is transmitted with the required level of reliability and latency.
- Network management: Monitoring and managing the performance and availability of the IIoT network.
Overall, the network layer is a critical component of IIoT architecture, as it enables seamless communication between devices and applications, and ensures that data is transmitted reliably and securely.
#3 Processing Layer:
The Processing layer consists of databases and servers and carries out operations such as decision-making, refining computation algorithms, and storing large volumes of data. These typically include data processing engines, data storage systems, and analytics tools to process data collected from industrial devices and sensors.
The key functions of the Processing layer an IIoT Solution include:
- Data aggregation: Collecting and consolidating data from various industrial devices and sensors.
- Data pre-processing: Filtering and cleaning the raw data to remove irregularities, redundant data, noise, and errors acquired from the Perception layer.
- Data analysis: Applying machine learning algorithms and other analytical techniques to derive insights from the data.
- Data storage: Storing the processed data in a suitable format for further analysis and retrieval.
- Data visualization: Presenting the insights derived from the data in a visually intuitive manner for users to understand.
The processing layer uses advanced technologies such as AI (Artificial Intelligence), ML (Machine Learning), Cloud computing, and Advanced analytics tools to make data insights more accessible and actionable for decision-makers.
For certain secure applications such as Military or Aerospace, where data processing needs to be done locally, on-field, the Processing layer uses Edge computing, a technology that enables data processing and analysis to be performed locally on edge devices, such as sensors and gateways, instead of transmitting all data to a central processing system. This reduces latency and improves the speed of decision-making in real-time industrial environments.
#4 Applications Layer:
The applications layer is the top layer of the IIoT architecture, and it is responsible for providing various applications and services that enable organizations to derive insights from the data collected by the perception layer to meet the application-specific needs of the end user.
The key functions of the Applications layer an IIoT Solution include:
- Data analysis: Applying advanced analytics techniques such as machine learning and predictive modeling to derive insights from the data.
- Data visualization: Presenting the insights derived from the data in a visually intuitive manner for users to understand.
- Process optimization: Using insights from the data to optimize industrial processes and improve efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance: Using machine learning algorithms to predict when industrial equipment is likely to fail, and proactively scheduling maintenance to avoid downtime.
- Asset tracking: Using real-time location tracking and monitoring to optimize the movement of assets in industrial environments.
- Quality control: Using machine vision and other advanced sensing technologies to monitor the quality of products in real-time.
The applications layer plays a critical role in enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions and optimize their industrial processes in real-time. A well-designed applications layer can help organizations to improve the efficiency of their operations, reduce downtime, and increase productivity.
Relevance of IIoT Four (4) Layer Framework for Industrial Automation across all Sectors:
By enabling organizations to collect, process, and analyze large amounts of data generated by industrial devices, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a powerful framework with the potential to transform industries with Automation. Here are some ways in which IIoT can be relevant across industries:
- Manufacturing: IIoT can enable real-time monitoring of production lines, improve product quality, reduce downtime, and optimize supply chain management.
- Power and Energy: IIoT can optimize energy usage, reduce waste, and improve the efficiency of energy production and distribution.
- Agriculture and Livestock: IIoT can help farmers optimize crop yields, reduce water consumption, and monitor environmental conditions to prevent crop damage.
- Healthcare: IIoT can enable remote monitoring of patients, improve patient outcomes, and reduce healthcare costs.
- Transportation/Mobility: IIoT can optimize transportation routes, reduce fuel consumption, and improve the safety of vehicles.
- Construction: IIoT can enable real-time monitoring of construction sites, improve worker safety, and reduce project timelines.
Conclusion:
Overall, a well-designed Industrial Automation solution, based on the IoT framework has the potential to transform various industries by providing real-time insights into industrial processes, optimizing performance, and improving efficiency. By leveraging IIoT, organizations can gain a competitive advantage, drive innovation, and create new business models that cater to the changing needs of their customers in their respective industries.
Note: When considering automating or integrating AI into your business, you must consult experts who can guide and advise you. Make sure to take all the necessary precautions to prevent further harm during this transition.
-Industry Digits Feed for IIoT and Industrial Automation
If you are passionate about staying informed of the newest intelligent automation products and technologies, our website is the perfect place for you! We post regular news and reviews to keep you up-to-date and provide a comprehensive range of resources for owners and decision-makers. From beginner tips through advanced advice, we have it covered – plus product recommendations so you can make an educated purchase decision.